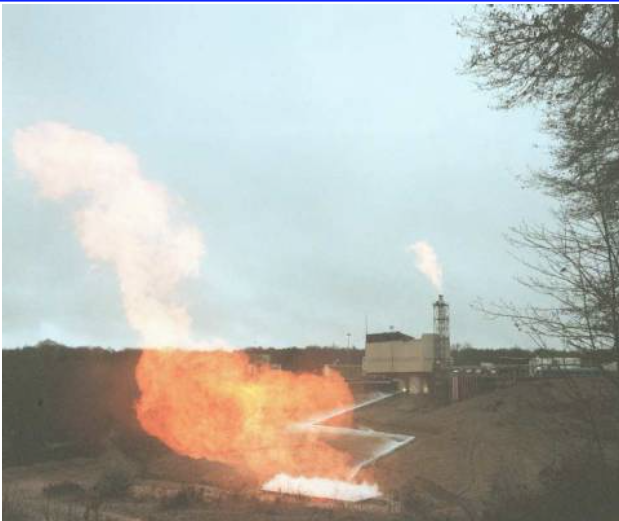

PF52 burn-off pool during test
Over and over and over again as the qualification tests on the Vinci® engine which will power the Ariane 6 upper stage were completed with the final 148th qualification test at ArianeGroup’s Vernon site.
Vinci® is a re-ignitable engine which contributes to the versatility of the Ariane 6 launcher, whose first flight is scheduled for 2020, since the final qualification test proved positive. The test was carried out on the PF52 test bench at ArianeGroup’s site in Vernon (France), and had a duration of more than 15 minutes (957 seconds) with two boosts.
This success, decisive for continuing the development of Ariane 6, ends the qualification test campaign, during which the Vinci® engine will have run for a total of 52,156 seconds (more than 14 hours).
These tests in Vernon followed the development/qualification tests in space vacuum conditions carried out in 2017 and 2018 on the P4.1 test bench of the German Aerospace Center (DLR) site in Lampoldshausen, Germany.
The qualifying campaigns have achieved several major ‘firsts’ in terms of performance, such as:
- a series of 20 successful consecutive boosts during a single test of 300 seconds
- a test with a total duration of 1,569 seconds
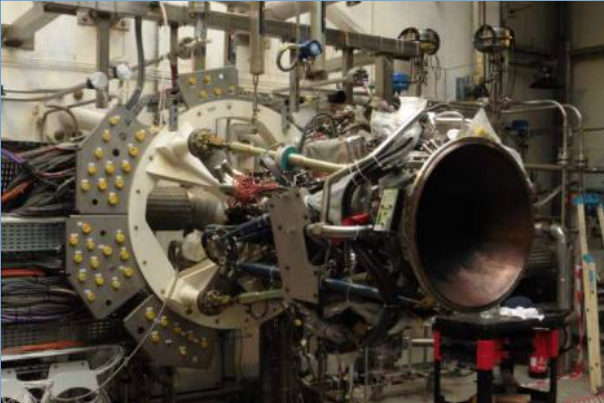
Vinci engine in test cell
The objective was to test the Vinci® engine beyond its operational requirements: during its missions, it will only need to be ignited up to four times, with a maximum burn time of 900 seconds in flight.
Alain Charmeau, CEO of ArianeGroup said that the conclusion of the Vinci engine qualification tests is a major step in the development of Ariane 6. It means that, from the beginning of 2019, ArianeGroup will be able to assemble in Vernon the first Vinci engine flight model, identical in configuration to the qualified model. It will then be integrated with the upper stage of the first Ariane 6 launcher flight model at the ArianeGroup site in Bremen, Germany.
At the same time, the production of the first parts of the Vinci® flight engines is underway at various ArianeGroup sites, with the combustion chambers at Ottobrunn in Germany, the divergent nozzles at Le Haillan near Bordeaux (France), and the hydrogen turbopumps at Vernon.
The Vinci® engine developed by ArianeGroup for Ariane 6 gives the future European launcher considerable versatility. Its main feature is its multiple ignition capability: Vinci® will be able to re-ignite as often as necessary to place several payloads into orbit at different locations, according to the specific requirements of the mission. This engine will enable the Ariane 6 launcher to carry out all types of missions, whatever their duration and target orbit, notably the deployment of satellite constellations, for which demand is continuing to grow.

