 [SatNews] The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is all set to deploy the crucial Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System or the IRNSS on June 12th, thus ushering in a new era in terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation services. Slated to be launched on board home-grown rocket PSLV-C22 XL at 1:01 a.m. from the Sriharikota spaceport, the IRNSS will help in disaster and fleet management as well.
[SatNews] The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is all set to deploy the crucial Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System or the IRNSS on June 12th, thus ushering in a new era in terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation services. Slated to be launched on board home-grown rocket PSLV-C22 XL at 1:01 a.m. from the Sriharikota spaceport, the IRNSS will help in disaster and fleet management as well.
The Standard Positioning Service of the satellite will help navigation services on land, air and water for civilian use, while the encrypted Restricted Service is meant ony for authorized users, such as the armed forces. The navigation system, which will also be used for tracking vehicles by law enforcement agencies, is housed in a 1425kg. satellite, with a life span of about 10 years. IRNSS has been developed at a cost of Rs 16 billion.
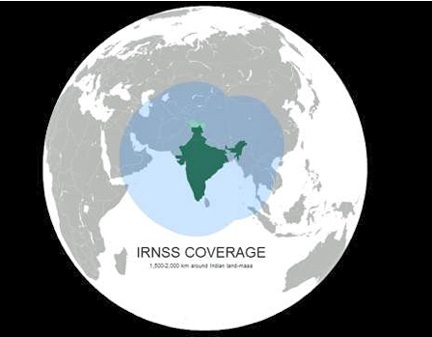
IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system, and at its peak operational capacity, it should provide positional accuracy of better than 10 metres over Indian territory and extending to about 1,500km around the country. The system will include a constellation of seven satellites under IRNSS by 2014-15. The fully-deployed IRNSS system will consist of three satellites in GEO (geostationary orbit) and four in the GSO (geosynchronous orbit), at approximately 36,000km above the earth's surface. Each satellite will be continuously monitored and maintained by a team of on-ground engineers. The navigation software of the satellite has been developed indigenously by ISRO engineers in Bangalore.

