
[SatNews] The first set of high-resolution results from ESA’s three-satellite Swarm constellation reveals the most recent changes in the magnetic field that protects our planet.
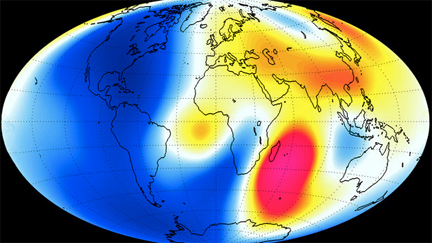
Magnetic field changes.
Image courtesy of ESA.
Launched in November 2013, Swarm is providing unprecedented insights into the complex workings of Earth’s magnetic field, which safeguards us from the bombarding cosmic radiation and charged particles. Measurements made over the past six months confirm the general trend of the field’s weakening, with the most dramatic declines over the Western Hemisphere. But in other areas, such as the southern Indian Ocean, the magnetic field has strengthened since January. The latest measurements also confirm the movement of magnetic North towards Siberia.
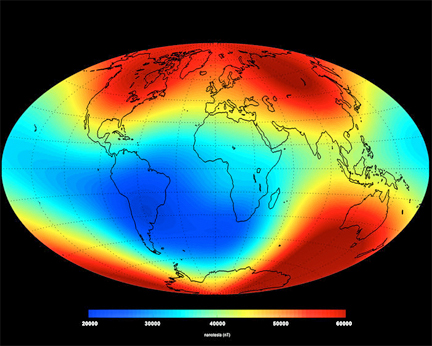
‘Snapshot’ of the main magnetic field at Earth’s surface as of June 2014 based on Swarm data. The measurements are dominated by the magnetic contribution from Earth’s core (about 95%) while the contributions from other sources (the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere) make up the rest. Red represents areas where the magnetic field is stronger, while blues show areas where it is weaker.
Image courtesy of ESA/DTU Space.
These changes are based on the magnetic signals stemming from Earth’s core. Over the coming months, scientists will analyse the data to unravel the magnetic contributions from other sources, namely the mantle, crust, oceans, ionosphere and magnetosphere. This will provide new insight into many natural processes, from those occurring deep inside our planet to space weather triggered by solar activity. In turn, this information will yield a better understanding of why the magnetic field is weakening.“These initial results demonstrate the excellent performance of Swarm,” said Rune Floberghagen, ESA’s Swarm Mission Manager. “With unprecedented resolution, the data also exhibit Swarm’s capability to map fine-scale features of the magnetic field.”
The first results have been presented at the ‘Third Swarm Science Meeting’ in Copenhagen, Denmark.
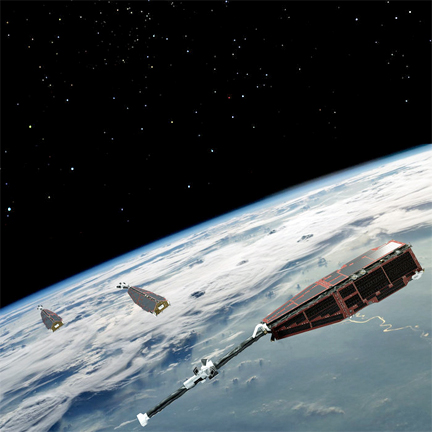

Swarm is ESA's first Earth observation constellation of satellites. The three identical satellites are launched together on one rocket. Two satellites orbit almost side-by-side at the same altitude – initially at about 460 km, descending to around 300 km over the lifetime of the mission. The third satellite is in a higher orbit of 530 km and at a slightly different inclination. The satellites’ orbits drift, resulting in the upper satellite crossing the path of the lower two at an angle of 90° in the third year of operations.
The different orbits along with satellites’ various instruments optimize the sampling in space and time, distinguishing between the effects of different sources and strengths of magnetism.
Image courtesy of ESA/AOES Medialab.
Sofie Carsten Nielsen, Danish Minister of Higher Education and Science, highlighted the Danish contribution to the mission. Swarm continues the legacy of the Danish Ørsted satellite, which is still operational, as well as the German Champ mission. Swarm’s core instrument—the Vector Field Magnetometer—was provided by the Technical University of Denmark.
Denmark’s National Space Institute, DTU Space, has a leading role—together with 10 European and Canadian research institutes—in the Swarm Satellite Constellation Application and Research Facility, which produces advanced models based on Swarm data describing each of the various sources of the measured field.
“I’m extremely happy to see that Swarm has materialized,” said Kristian Pedersen, Director of DTU Space.
The ESA infosite is located at http://www.esa.int/

