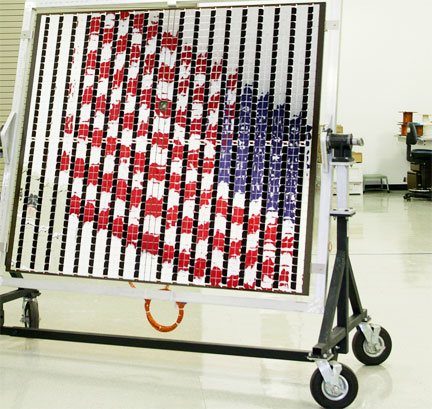
Northrop Grumman's MESSENGER sollar array, photo courtesy of the company.
Link to the Company homepage

NASA's MESSENGER satellite, artistic rendition
Solar array performance is critical – if it fails, so does the mission. Two single-sided solar panels are MESSENGER's main source of electrical power. They are two-thirds mirrors and one-third solar cells. The mirrors reflect the sun's energy and keep the panels cooler. The panels also rotate away from the sun to get the required power and maintain an operating temperature of about 300 F. Since its launch, MESSENGER has completed one swing past Earth, two Venus flybys and three Mercury flybys. By using the gravity of each planet to gain speed and alter its trajectory, MESSENGER was able to conserve the fuel it will need during its mission orbiting a planet that is only 29 million miles from the sun, about two thirds closer to the sun than Earth. At Mercury's equator, surface temperatures become hot enough to melt lead. The spacecraft's fast, elliptical orbit allows it to approach Mercury, gather data and swing out far into space to cool down.

